•
Interest rate cycles have
peaked both globally and in
India.
• Investors should add duration
with every rise in yields.
•
Mix of 10-year duration and
2-4-year duration assets are
best strategies to invest in the
current macro environment.
•
Credits continue to remain
attractive from a risk reward
perspective given the improving
macro fundamentals.
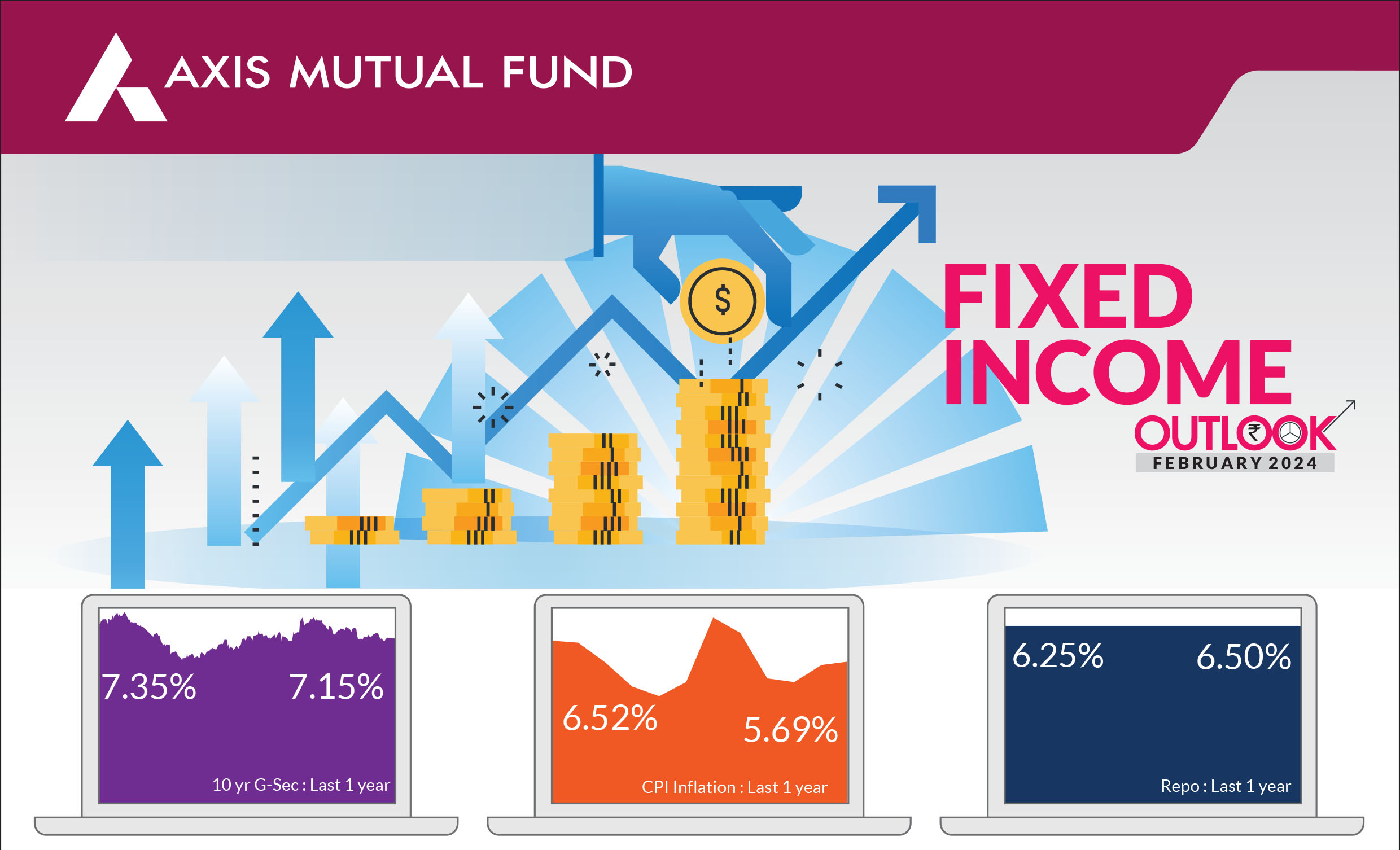
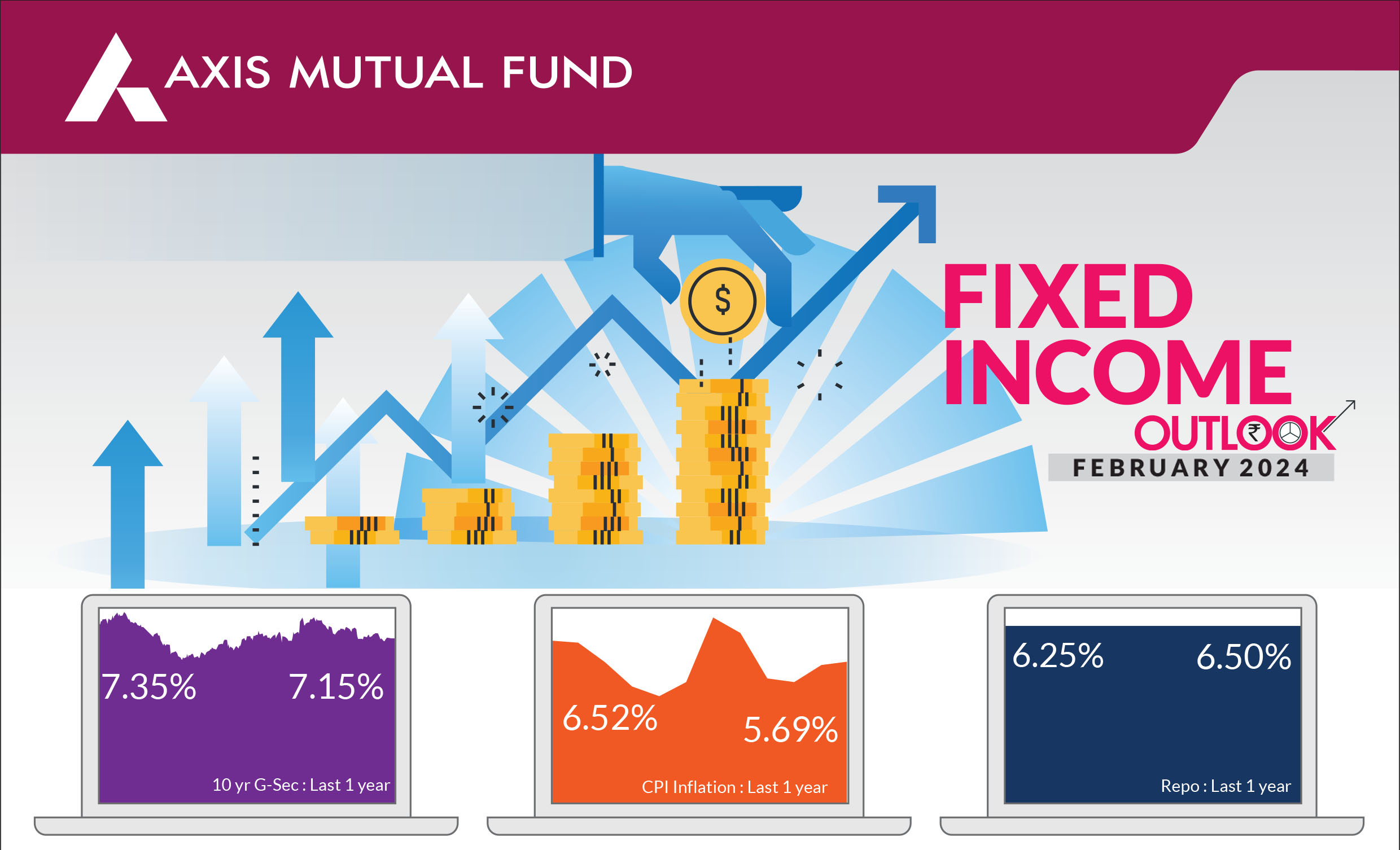
The key factors driving the bond markets were expectations from the Interim Budget and expectations that the central banks across the globe would start lowering interest rates soon. Indian government bond yields fell for the third consecutive month, trading in a narrow band of 7.15-7.23% and ending at 7.15%. Post the interim budget announcement, 10 year bond yields fell to 7.05% levels.
► Global interest rate environment:
US Treasury yields were higher
over the previous month, and
touched an intra month high of
4.18% before receding to 3.91%
ahead of the interest rate decision
by the Federal Reserve. In contrast,
yields on the 2 year Treasuries fell 4 bps. In its January policy meeting, the Fed
maintained rates on hold for the fourth consecutive time but noted that it
won't be appropriate to cut rates until it has gained greater confidence that
inflation is approaching its 2% goal. The European Central Bank is also
expected to lower the interest rates around the same time as Fed.
China cut the reserve requirement ratio for banks from early February to unleash more money and help the economy. A 0.5% cut to the ratio, the amount of cash that banks have to keep in reserve, will provide 1 trillion yuan ($139 billion) in long-term liquidity to the market. However, economic data is not as encouraging and investor confidence remains low. Meanwhile, the central bank of Japan is likely considering an exit in the near term from its massive stimulus programs and getting out of negative interest rate regime.
China cut the reserve requirement ratio for banks from early February to unleash more money and help the economy. A 0.5% cut to the ratio, the amount of cash that banks have to keep in reserve, will provide 1 trillion yuan ($139 billion) in long-term liquidity to the market. However, economic data is not as encouraging and investor confidence remains low. Meanwhile, the central bank of Japan is likely considering an exit in the near term from its massive stimulus programs and getting out of negative interest rate regime.

► Inflationary pressures and oil prices rise:
CPI rose slightly to 5.7% YoY in
December, even as core CPI moderated further to 3.9%. Though food prices
increased, incoming data reflects softening of food prices in January,
especially onions, aided by the government's proactive supply-side
management. Oil prices rose 6% over the month and briefly crossed the $83
mark. In the region, attacks by Yemen's Houthi forces on vessels in the Red
Sea have continued to disrupt global trade, spurring geopolitical tensions and
shipping concerns and also increasing freight rates.
► Interim budget positive for bond markets:: In its Interim Budget on 1 February, the government projected a fiscal deficit of 5.1% of GDP for 2024- 25, adhering to its path of fiscal consolidation. Further it lowered the FY24 fiscal deficit to 5.8% of GDP (vs. 5.9% of GDP as per budget estimates). The government also spelled out its gross and net market borrowing which were albeit lower than FY24. The gross market borrowings will be Rs 14.13 lakh crore and net borrowing would be Rs 11.75 lakh crore. The capex outlay has been another area of focus where the outlay has been increased to 11.11 lakh crore, up 11.1% for FY24, ie 3.4% of GDP.
► Macro indicators remain steady: Domestic demand witnessed some amount of moderation in December, even as absolute levels of activity remain healthy. GST collections for December slowed to Rs 1.65 tn, growing 10.7% annually, while Manufacturing PMI declined to 54.9, even as it remains in an expansionary mode since July 2021. On the external demand front, exports grew 1% in December vs -2.9% in the previous month.
► Interim budget positive for bond markets:: In its Interim Budget on 1 February, the government projected a fiscal deficit of 5.1% of GDP for 2024- 25, adhering to its path of fiscal consolidation. Further it lowered the FY24 fiscal deficit to 5.8% of GDP (vs. 5.9% of GDP as per budget estimates). The government also spelled out its gross and net market borrowing which were albeit lower than FY24. The gross market borrowings will be Rs 14.13 lakh crore and net borrowing would be Rs 11.75 lakh crore. The capex outlay has been another area of focus where the outlay has been increased to 11.11 lakh crore, up 11.1% for FY24, ie 3.4% of GDP.
► Macro indicators remain steady: Domestic demand witnessed some amount of moderation in December, even as absolute levels of activity remain healthy. GST collections for December slowed to Rs 1.65 tn, growing 10.7% annually, while Manufacturing PMI declined to 54.9, even as it remains in an expansionary mode since July 2021. On the external demand front, exports grew 1% in December vs -2.9% in the previous month.
Market view
Inflation is fading globally giving way to increased expectations of interest rates cuts. Growth is slowing down too although US is still being defiant on certain fronts. This lower inflation and benign growth will be the trigger for central banks to lower interest rates. Markets were anticipating the rate cuts as early as March and the Fed's latest policy speak has pushed these expectations to April 2024. The committee said it does not have enough good inflation data to lower rates in March. We believe that the Fed is in no hurry to cut interest rates and perhaps will look at April-June 2024 as more data shows inflation and the economy is slowing down. We also believe that the European Central Bank could lower interest rates around the same time as Fed. Furthermore, even the RBI is more likely to take cues from the Fed and the ECB.The interim budget on 1 February outlines the path of fiscal consolidation. The budget was cheered by the debt markets. The yields on the 10 year government bond fell 10 bps post the budget. The lower fiscal deficit figure of 5.1% vs market expectations of 5.3-5.4% has been a positive for the markets. Furthermore, the lower gross market borrowings is another positive. These coupled with the expected inflows in JP Morgan Indices Index will help bring down yields further lower. We believe that the budget has given a breather to the RBI to ease its liquidity stance to neutral, maintain status quo and move its operative rate back to 6.5% through pro-active measures such as VRR auctions, temporary ICRR cut on deposits and other liquidity measures in the interim.
Positioning & Strategy
Most part of the fixed income curve is pricing in cuts only after June 2024. With policy rates remaining incrementally stable, we have retained our long duration stance across our portfolios within the respective scheme mandates. We do expect the 10-year bond yields to touch 6.75% by June 2024.
From a strategy perspective, we continue to add duration across portfolios within the respective investment mandates. We expect our duration call to add value in the medium term. Investors could use this opportunity to top up on duration products with a structural allocation to short and medium duration funds and a tactical play on GILT funds.
Source: Bloomberg, Axis MF Research.